By integrating pneumatics technologies, consumer packaged goods companies can reduce their carbon — and equipment — footprint.
Contributed by Mark Densley, Director Business Development Factory Automation, Emerson
Customer demand, as well as a sense of environmental responsibility, is driving consumer packaged goods (CPG) companies to drastically reduce their carbon footprint. While many companies seek ways to make their packaging material more sustainable, they can also save a significant amount of energy by monitoring pneumatic components in their packaging lines.

Cost-effective and compact, pneumatics has been a steadfast technology in the consumer products market for years, playing a vital role in a wide range of packaging systems. However, they are now go-to components for even more reasons: These proven solutions have valuable capabilities as well as comprehensive, actionable data that can optimize energy use, improve overall equipment efficiency and maximize performance.
Here are two ways in which CPG companies can integrate pneumatics into packaging lines to reduce their carbon footprint and deliver a more compact, greener packaging line.
Compressed air
Compressed air is used to help operate equipment and power processes throughout packaging lines, including bottle production. While its prevalence can mean a high potential for energy loss, the right tools can turn it into a valuable opportunity for energy savings.
Not long ago, there was no reliable way to evaluate compressed air consumption. The digital transformation of pneumatics has changed that. Today’s smart pneumatic devices provide a more complete picture of pneumatic system performance as well as actionable insights that give companies the ability to better understand and effectively control the energy use of their packaging lines.
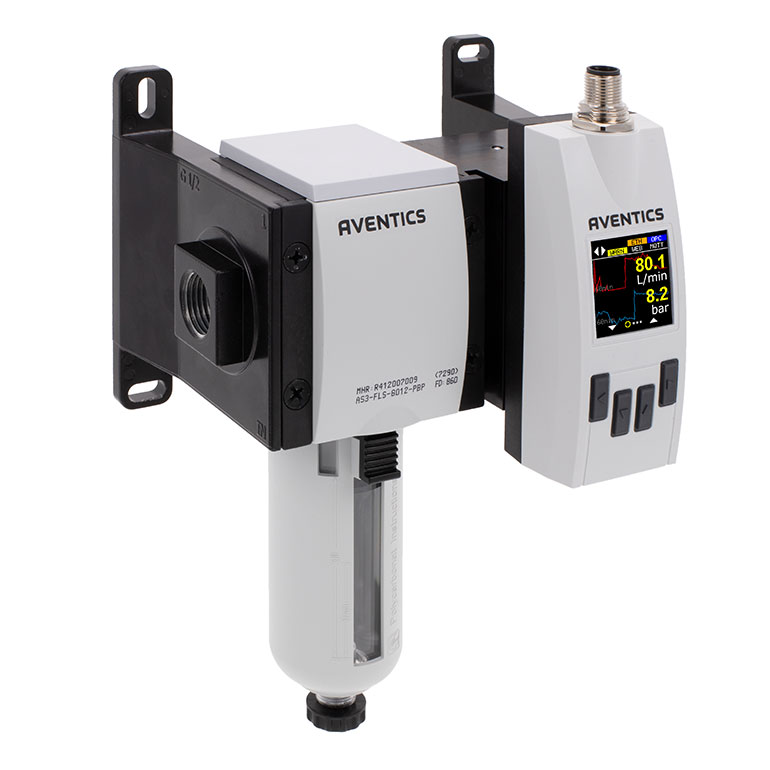

Smart sensors, combined with an edge computing device, can continuously monitor system airflow and capture real-time flow, pressure and actuator speed. When properly analyzed, this data can help detect leaks and optimize compressed airflow, as seen in Figure 1.
Using the edge analytics, operators can see the relationship between air pressure, flow and the speed of the actuator more clearly. By better understanding the true nature of this relationship, operators can determine the optimal consumption point of compressed air for their packaging processes.
If the analyzed incoming pressure is higher than a process requires, and more compressed air is being used than needed, operators can reduce the pressure and modulate airflow while maintaining the same cylinder cycle time. By optimizing the amount of compressed air to meet operational requirements without affecting production, companies can minimize energy use.
In addition to optimizing compressed air use, software monitoring can also help operators detect leaks in near-real time. Once it detects a leak, the monitoring system sends an alert to maintenance personnel, who can then investigate the equipment in question. In this way, operators can address compressed air leaks much sooner, preventing compressed air loss and reducing emissions, Figure 2.
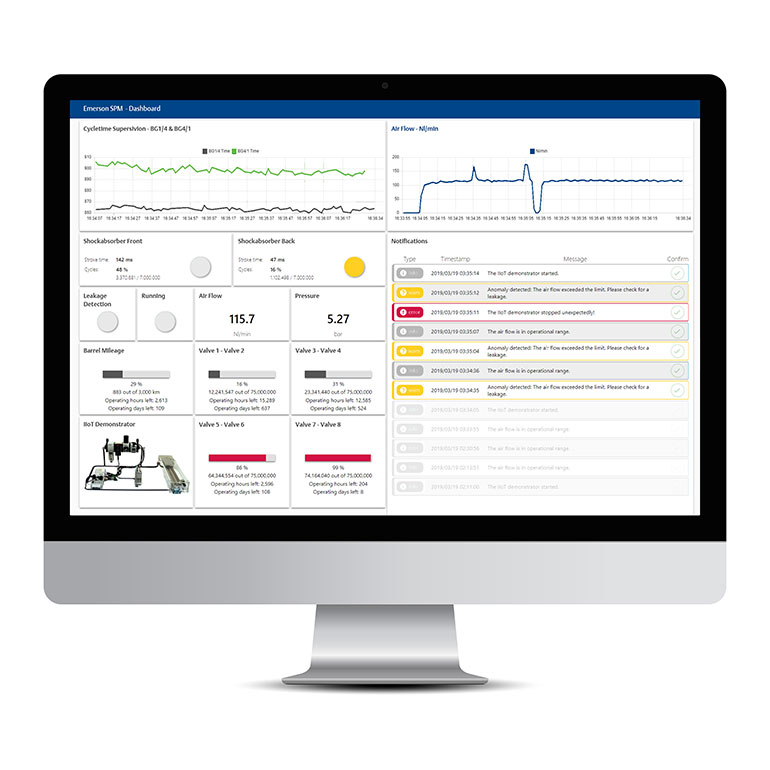
Depending on the size and nature of the machinery being monitored, companies can typically save 10-20% in compressed air energy costs and see a carbon footprint reduction of up to 10% through early leak detection and optimized air consumption.
System monitoring can help reduce downtime and improve overall equipment efficiency (OEE), too. Companies no longer need to plan downtime and have technicians test each machine for leaks, and leaks are sealed before they can cause fluctuations in system pressure. Leak-related fluctuations can make machines cycle more than needed, and this extra work wastes energy, prematurely wears equipment and components and increases maintenance.
PET bottle production
The polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottle is the most widely used bottling product in the world. It is so popular, about 3,500 stretch blow molding (SBM) systems are built and deployed annually to meet demand. The latest systems combine the SBM process with the bottling process in one continuous production flow. This combination production system obviously makes lines more compact and reduces a bottler’s carbon footprint by eliminating the shipping step that occurred between bottle production and filling. Pneumatic technology is a key part of their construction.
Pneumatics powers several key areas of SBM machines. Pneumatic air preparation systems improve efficiency and offer better control of the low- and high-pressure air that preform actuators and stretch blow bottle expansion steps use. And compact, high-performance blowing blocks provide bottle volume growth control through pre-blow, blow, recycling and exhaust functions.
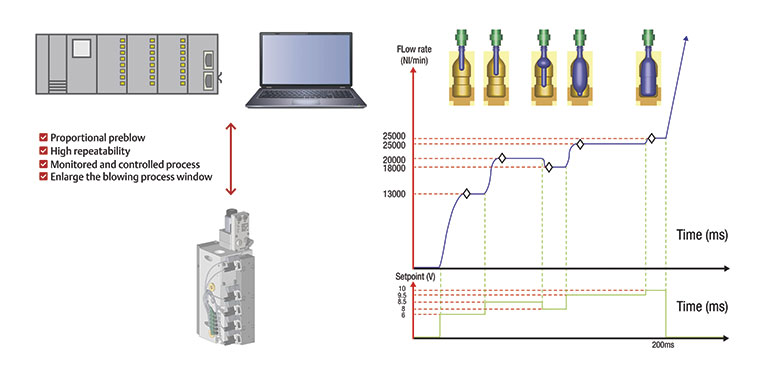
Some suppliers have advanced SBM pneumatic performance, and sustainability, even further. For example, Emerson offers a proportional control valve developed for the pre-blow expansion step in PET production that replaces an on/off high-pressure flow and, quite honestly, revolutionizes this bottle production step. Where the previous on/off high-pressure flow set a uniform flow rate throughout the blow process, the new control modulates the flow to fine-tune each bottle’s expansion within the mold, as indicated in Figure 3.
This advanced proportional valve technology combines a specially designed proportional valve, control electronics, and software, which can either store the blowing sequence setpoints in the valve or respond to control directions from the stretch blow molding (SBM) programmable logic controller (PLC) that directs the blowing process. The resulting bottle grow is intelligently modulated, giving end users the ability to perfect how the heated bottle expands within the mold.
The system can also capture feedback results for the quality of each blow, providing critical data needed by bottle manufacturers to perfect the process and minimize the number of rejected, wasted bottles. It also provides condition monitoring data to support routine and preventive maintenance programs.
Proportional technology for PET blowing moves pneumatics to a whole new level of sustainability for this process. It offers the potential to reduce material consumption with the capability to fine-tune bottle wall and shape formation, to create thinner, more lightweight containers. It also saves energy by potentially reducing blow air pressure required for high-quality bottle formation and by reducing the heating temperature in the pre-blow oven.
In addition to its energy saving benefits, proportional technology for PET blowing also enables the high throughput production of more complex bottle shapes, which is a critical goal for a bottler’s marketing purposes. It also increases manufacturing flexibility, since the process can be easily changed via software/PLC formula specific to each blowing station on the machine and fine-tuned for further improvement without stopping production.
Conclusion
Consumer packaged goods companies have long counted on pneumatics as an effective, reliable machine technology to package items from soda bottles and cereal boxes to single-serve snack pouches and pharmaceutical blister packs. And the latest advances in pneumatics, including the digital transformation of the packaging line, promise even greater benefits.
While the right technology will power greener, more compact packaging lines, it’s important that CPG companies work with an automation expert who understands smart pneumatics and the distinct characteristics of fluid power applications to achieve their most ambitious sustainability and performance goals. By using a range of pneumatic technologies, including smart pneumatics, companies have the potential to significantly reduce their carbon footprint — while considerably improving OEE.
Emerson | emerson.com
Filed Under: Pneumatic Tips, Trending, Valves & Manifolds