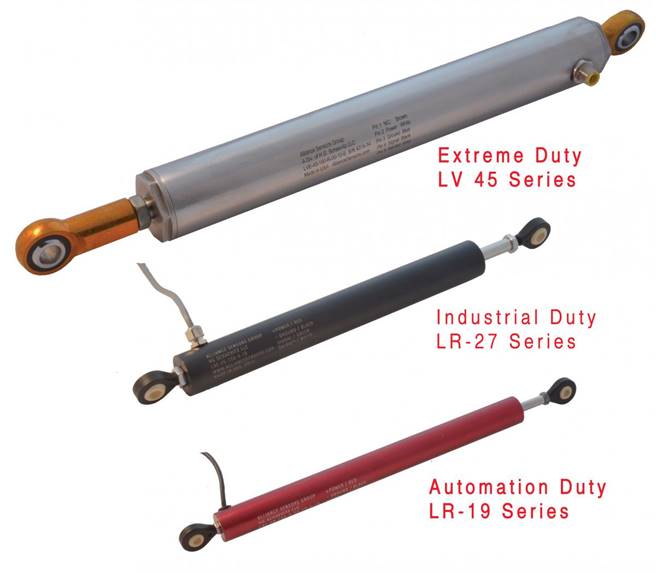
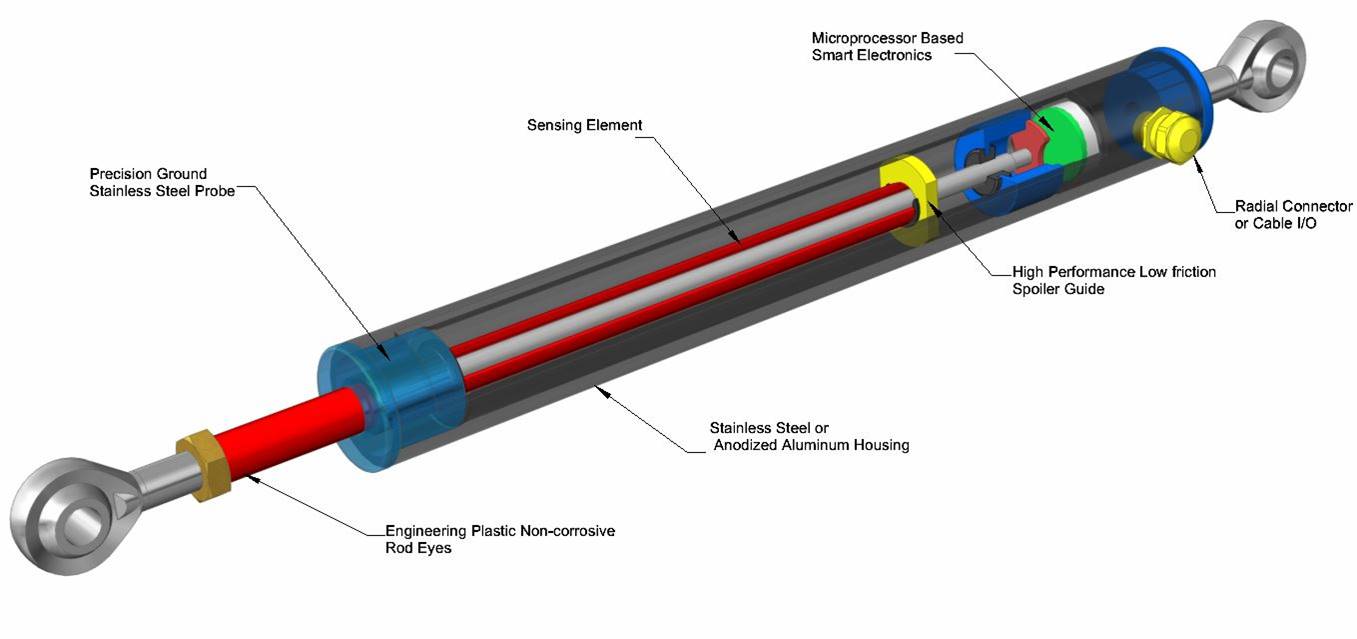
 LVITs—Linear Variable Inductive Transducers—have been around for more than 30 years, and are becoming very popular, due to their relatively low cost and flexibility to be packaged in many different forms. LVITs are contactless position sensing devices. They use eddy currents developed by an inductor in the surface of a conductive movable element to vary the resonant frequency of an L-C tank circuit. The most common form of an LVIT uses a small diameter inductive probe surrounded by a conductive tube called a spoiler that is mechanically coupled to the moving object. Typical LVITs have full ranges from fractions of an inch to 30 in. or more. Modern electronics using microprocessors and small component size makes outstanding performance possible, achieving linearity errors of less than ±0.1% and temperature coefficients of 50 ppm/°F, along with either analog or digital outputs. The range of housing sizes for LVITs can be seen in Figure 1 and a cutaway view of an LVIT can be seen in Figure 2.
LVITs—Linear Variable Inductive Transducers—have been around for more than 30 years, and are becoming very popular, due to their relatively low cost and flexibility to be packaged in many different forms. LVITs are contactless position sensing devices. They use eddy currents developed by an inductor in the surface of a conductive movable element to vary the resonant frequency of an L-C tank circuit. The most common form of an LVIT uses a small diameter inductive probe surrounded by a conductive tube called a spoiler that is mechanically coupled to the moving object. Typical LVITs have full ranges from fractions of an inch to 30 in. or more. Modern electronics using microprocessors and small component size makes outstanding performance possible, achieving linearity errors of less than ±0.1% and temperature coefficients of 50 ppm/°F, along with either analog or digital outputs. The range of housing sizes for LVITs can be seen in Figure 1 and a cutaway view of an LVIT can be seen in Figure 2.
 LVITs are found in a wide variety of different applications that require position information or feedback. Typical LVIT applications include mobile hydraulics, subsea hardware, civil engineering testing and factory automation.
LVITs are found in a wide variety of different applications that require position information or feedback. Typical LVIT applications include mobile hydraulics, subsea hardware, civil engineering testing and factory automation.
In mobile hydraulics, the LVIT is commonly used to measure hydraulic or pneumatic cylinder position. Usually the sensor has a pressure-sealed head and a probe long enough to insert into a gun-drilled hole in the cylinder’s ram. The ID of this hole in the ram then acts as the spoiler. The sensor head can either be port mounted or embedded into the end cap of the cylinder. A typical in-cylinder LVIT installation is shown in Figure 3.
 This packaging fulfills many different applications in mobile hydraulics such as bulldozer shovel or snow plow positioning, boom positioning on hydraulic cranes and manlifts, and in a variety of agricultural vehicle accessory position feedback requirements
This packaging fulfills many different applications in mobile hydraulics such as bulldozer shovel or snow plow positioning, boom positioning on hydraulic cranes and manlifts, and in a variety of agricultural vehicle accessory position feedback requirements
For subsea cylinder applications involving pumps, chokes, blowout preventers, and ROV-based actuators, the LVIT is designed to withstand the internal and/or external pressures of a PBOF (pressure balanced, oil filled) system. Other technologies commonly used to satisfy these applications require additional hardware like a ring magnet to operate, which adds cost to the machining of the cylinder ram and complexity to the installation. Typical subsea LVITs are shown in Figure 4.
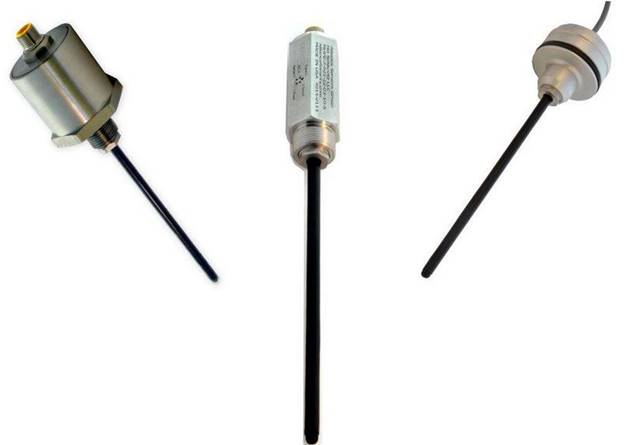 LVITs are used in many factory automation applications, including packaging and material handling equipment, die platen position in plastic molding machines, roller position and web tension controls in paper mills or converting facilities, and robotic spray painting systems. Being contactless, the basic measurement mechanism of an LVIT does not wear out over time. LVITs also do not have the higher installed cost associated with other contactless technologies.
LVITs are used in many factory automation applications, including packaging and material handling equipment, die platen position in plastic molding machines, roller position and web tension controls in paper mills or converting facilities, and robotic spray painting systems. Being contactless, the basic measurement mechanism of an LVIT does not wear out over time. LVITs also do not have the higher installed cost associated with other contactless technologies.
Alliance Sensors Group
https://alliancesensors.com
Filed Under: Mobile Hydraulic Tips, Sensors