Contributed by Chuck White, Director of Sales & Marketing, Hallite
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is widely used in fluid power seal applications and is a family of polymers formed using a combination of isocyanate and polyol crosslinked to create a homogeneous compound polymer. There are many different combinations of these chemicals that may be used to form the best TPU for the sealing application. Overall, TPUs are ideal for sealing as the material has high abrasion and extrusion resistance while offering a high level of sealability. TPU is typically processed as pellets that are injection molded, although some polyurethanes (thermoset) are cast from thick prepolymer liquids. Having these process options allows for the creation of billets that can be machined to create a variety of seal profiles or injection molded to support higher volumes.
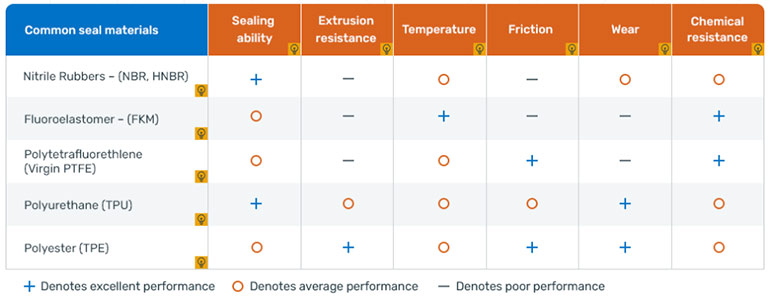
Figure 1 – Seal material characteristics – pros and cons (reference Halite Fluid Power 201 training platform)
Choosing the right TPU for the application is essential to ensure optimized seal function in defined conditions. For example, if seals will be operating in a cold environment, using a TPU with a combination of an MDI (Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate) and PTMEG (polytetramethylene Ether Glycol) polyol may provide the best performance. However, using this combination will limit high temperature operation. On the other hand, using a PPDI (p-phenylene diisocyanate) and polycarbonate polyol will allow use at much higher temperatures, but this combination greatly reduces material’s ability to perform at lower temperatures. As a solution, seals are manufactured in a variety of materials for different operating conditions.
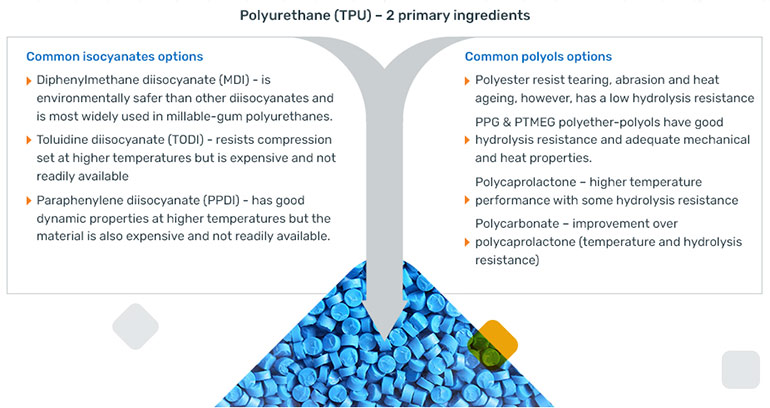
Figure 2– Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) primary ingredients (reference Halite Fluid Power 201 training platform)
Another consideration is hydrolysis resistance of the sealing material. Depending on the base ingredients, TPUs can be configured to operate in non-mineral oil-based hydraulic fluids, if the temperature is maintained at a reasonable level. TPUs that utilize a PTMEG, or polycarbonate polyol are best suited to operate in these types of fluids. If operation at higher temperatures is a must, a combination of a PPDI isocyanate and polycarbonate polyol may make this possible; however, this combination is less available and more costly. This is an important consideration as the industry drives towards more environmentally friendly fluids that range from use of synthetic esters to water/glycol formulations. Again, this is the reason why seals are manufactured in a range of materials to offer the best fit for the application.
TPU provides a wide range of options when it is used in sealing applications. Of all the materials used to produce fluid power seals, TPUs offer the most flexibility as optimized performance characteristics can be accessible by ensuring the correct chemistry of the combination of key ingredients. Nevertheless, in sealing applications, no single material can do everything or fit all applications, but with the flexibility of TPU blends, materials can be produced to fit a wider range of applications.
Hallite
hallite.com
Filed Under: Engineering Basics, Sealing, Sealing & Contamination Control Tips